Laser For Frequency Comb is an example of the integrated use of a feedback control system to lock onto and track a desired output signal. The feedback control system compares the voltage produced by the instrument’s laser diode with a reference voltage, and adjusts the optical characteristics of another element in the instrument in order to compensate for any difference.
Frequency Comb Laser is a type of laser that is used for home theater systems. Where it uses its laser power to generate the color of light, it also increases the audio levels inside the theater. This improves audio and video experience to an alternative level. Its wonderful design and fitting can be fixed in any room of your house. And you can play move with its help in your home theater system.

Laser For Frequency Comb
A laser for frequency comb is a laser that emits a very specific, calibrated spectral distribution of frequencies. A frequency comb is a laser whose output is periodic in wavelength. The term “comb” refers to the spacing of the spectral lines produced by the laser.
Frequency combs are used in spectroscopy and signal processing applications, where they provide high-resolution spectral analysis at low cost and high speed.
The frequency comb is a very useful device that can be used in many different applications. It has been used in quantum information research and quantum optics experiments. It has also been used to generate ultra-high-precision clocks, which could be used for navigation and timing applications.
The frequency comb is a laser with many frequencies that are separated by the same distance. Since there are many frequencies, it is possible to measure the distance between them using a spectrometer. The spectrum of the frequency comb can be easily adjusted by changing the temperature or power of the lasers, making it possible to use this device as an accurate tool for measuring time and distance.
In general, lasers are not suitable for long-term measurements because they have a very narrow spectral width and cannot be tuned over large spectral ranges. However, this problem can be solved by using a frequency comb instead of a single laser source with narrow spectral widths.
Frequency combs are used in many different types of laser technology because of their unique properties. They can be created with different types of lasers, but the most common type uses a nonlinear optical medium such as lithium niobate (LiNbO3) or potassium titanyl phosphate (KTP). When light enters the material at high enough intensity levels, it causes some of it to convert into higher frequencies than those that originally entered the material. This phenomenon is called second-harmonic generation (SHG). It occurs when photons interact with an electric field at right angles with respect to each other, creating new photons with double the frequency. This effect can be repeated several times, creating even higher frequencies until there are too many for the material.
Optical Frequency Comb Applications
Optical Frequency Comb Applications
The optical frequency comb is a powerful technique for measuring the frequency of light. It can be used to measure both high-frequency and low-frequency sources, with excellent accuracy and precision. The technique is also used for generating stable and highly accurate frequencies for driving lasers and other optical devices.
Optical frequency combs are used in many scientific applications including:
Metrology
Precision measurement of atomic transitions is an important part of modern science. Atomic clocks are among the most accurate time standards available today. Optical frequency combs have been shown to be able to provide an even higher level of precision than current atomic clocks by making use of their greater resolution.
Astronomy
Astronomers use optical frequency combs to map the positions of stars and other objects in space with extreme accuracy. This information can be used by astronomers to study the movements of celestial bodies over long periods of time, helping them to determine their orbits and other characteristics such as temperature, density and age. Astronomical measurements made using optical frequency combs have provided new insights into how stars form, evolve and die.
An optical frequency comb is a set of discrete optical frequency tones that are equally spaced in frequency. The spacing between adjacent frequency tones is referred to as the comb spacing. The frequencies of each tone in the set can be easily tuned by changing the length of a Fabry–Pérot cavity, which is an optical resonator made from two mirrors, one partially transmitting and one partially reflective.
Optical frequency combs are used in many applications, including spectroscopy, telecommunications, and quantum information science. In spectroscopy and telecommunications applications, they are used to generate narrow-linewidth optical references for use in lasers and detectors. In quantum information science applications, they are used for generating quantum entanglement between different atomic species and for quantum metrology.
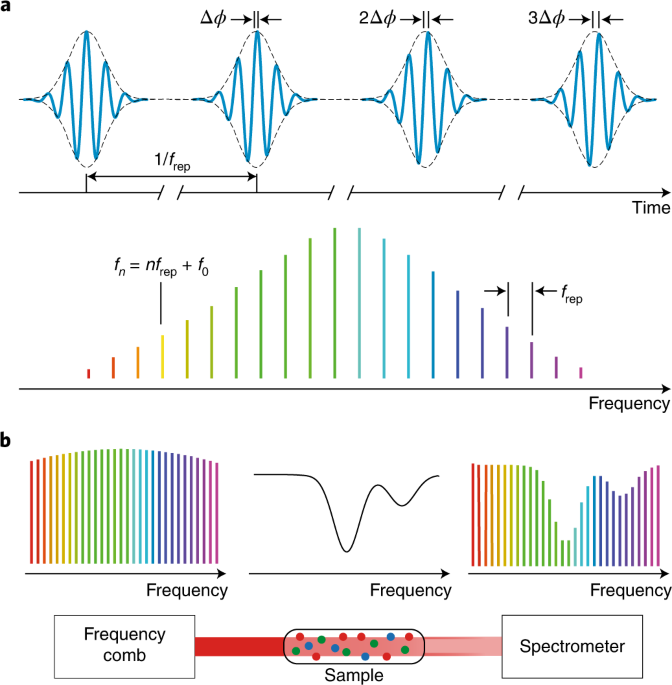
Frequency Comb Spectroscopy
Frequency Comb Spectroscopy
The frequency comb is an optical frequency reference that generates a series of evenly spaced optical tones, each separated by the same frequency. This can be used as a time-of-flight (TOF) spectral interferometry technique with high sensitivity, fast acquisition speed and large spectral range. The frequency comb spectrometer (FCS) is the counterpart of the FCS in radio astronomy. It is based on an optical source that provides light at a high repetition rate and at a very stable frequency to drive a dispersive element such as an etalon or a grating. The combination of these two elements allows the generation of light at different wavelengths within the visible or near infrared spectrum. In comparison to commercial spectrometers based on nonlinear gratings and lasers or diode arrays, which provide high spectral resolution but only low throughputs, FCSs provide both high throughput and high resolution over a wide spectral range without requiring any mechanical motion of the sample stage.
Frequency comb spectroscopy (FCS) is a type of spectroscopy that uses frequency combs to measure the spectrum of a sample. It is used in applications such as atomic clocks and metrology, as well as in fundamental science research.
In FCS, the light from a laser source is divided into many frequency components using a diffraction grating or prism. These components are sent through a dispersive element (such as a prism) which causes them to separate in time due to their different frequencies. The resulting spectrum can be analyzed using Fourier transform techniques to determine the amplitude and phase of each frequency component.