What To Know About Chemical Peel Scars
Scarring from a chemical peel: What You Need to Know. One of the most common forms of cosmetic treatment for acne scars, age spots, and wrinkles, chemical peels have gained popularity in recent years. Nonetheless, you should be aware that scarring might result from improperly executed chemical peels.
If you’re considering getting a chemical peel, it’s important to arm yourself with information about the potential side effects, including scarring, before you schedule your appointment.
A chemical peel is a cosmetic procedure used to treat different types of scars. A doctor uses chemicals to remove skin impurities, enhance skin complexion and correct facial flaws in order to achieve glowing skin. The chemicals remove dead skin cells, stimulate growth of new cells and remove imperfections like brown spots. With chemicals, blemishes are removed, congestion is reduced and pigmentation is evened out in just one session. Here’s what you need to know about chemical peel scars. Read on to learn more on chemical peel for scars on legs and chemical peel benefits.

What To Know About Chemical Peel Scars
A chemical peel is a skin-resurfacing procedure. Depending on the issues you’re addressing with the procedure, you’ll choose a chemical peel in one of three depths:
- Light chemical peel. A light (superficial) chemical peel removes the outer layer of skin (epidermis). It’s used to treat fine wrinkles, acne, uneven skin tone and dryness. You might have a light peel every two to five weeks.
- Medium chemical peel. A medium chemical peel removes skin cells from the epidermis and from portions of the upper part of your middle layer of skin (dermis). It’s used to treat wrinkles, acne scars and uneven skin tone. You might need to repeat the procedure to achieve or maintain the desired result.
- Deep chemical peel. A deep chemical peel removes skin cells even deeper. Your doctor might recommend one for deeper wrinkles, scars or precancerous growths. You won’t need repeat procedures to get the full effect.
Chemical peels can’t remove deep scars or wrinkles or tighten sagging skin.
Request an Appointment at Mayo Clinic
Risks
A chemical peel can cause various side effects, including:
- Redness, scabbing and swelling. Normal healing from a chemical peel involves redness of the treated skin. After a medium or deep chemical peel, redness might last for a few months.
- Scarring. Rarely, a chemical peel can cause scarring — typically on the lower part of the face. Antibiotics and steroid medications can be used to soften the appearance of these scars.
- Changes in skin color. A chemical peel can cause treated skin to become darker than normal (hyperpigmentation) or lighter than normal (hypopigmentation). Hyperpigmentation is more common after superficial peels, while hypopigmentation is more common after a deep peel. These problems are more common in people with brown or black skin and can sometimes be permanent.
- Infection. A chemical peel can lead to a bacterial, fungal or viral infection, such as a flare-up of the herpes virus — the virus that causes cold sores.
- Heart, kidney or liver damage. A deep chemical peel uses carbolic acid (phenol), which can damage heart muscle and cause the heart to beat irregularly. Phenol can also harm the kidneys and liver. To limit exposure to phenol, a deep chemical peel is done a portion at a time, in 10- to 20-minute intervals.
A chemical peel isn’t for everyone. Your doctor might caution against a chemical peel or certain types of chemical peels if you:
- Have taken the oral acne medication isotretinoin (Myorisan, Claravis, others) in the past six months
- Have a personal or family history of ridged areas caused by an overgrowth of scar tissue (keloids)
- Are pregnant
- Have frequent or severe outbreaks of cold sores
How you prepare
Choose a doctor with knowledge of the skin and procedure — a dermatologist or dermatologic surgeon. Results can be variable and depend on the expertise of the person doing the peel. Improperly done, a chemical peel can result in complications, including infection and permanent scars.
Before you have a chemical peel, your doctor will likely:
- Review your medical history. Be prepared to answer questions about current and past medical conditions and any medications you are taking or have taken recently, as well as any cosmetic procedures you’ve had.
- Do a physical exam. Your doctor will inspect your skin and the area to be treated to determine what type of peel you might benefit from most and how your physical features — for example, the tone and thickness of your skin — might affect your results.
- Discuss your expectations. Talk with your doctor about your motivations, expectations and potential risks. Make sure you understand how many treatments you might need, how long it’ll take to heal and what your results might be.
Before your peel, you might also need to:
- Take antiviral medication. Your doctor might prescribe an antiviral medication before and after treatment to help prevent a viral infection.
- Use a retinoid cream. Your doctor might recommend using a retinoid cream, such as tretinoin (Renova, Retin-A) for a few weeks before treatment to help with healing.
- Use a bleaching agent. Your doctor might recommend using a bleaching agent (hydroquinone), a retinoid cream, or both before or after the procedure to reduce the risk of side effects.
- Avoid unprotected sun exposure. Too much sun exposure before the procedure can cause permanent irregular pigmentation in treated areas. Discuss sun protection and acceptable sun exposure with your doctor.
- Avoid certain cosmetic treatments and certain types of hair removal. About a week before the peel, stop using hair removal techniques such as electrolysis or depilatories. Also, avoid hair dying treatments, permanent-wave or hair-straightening treatments, facial masks, or facial scrubs in the week before your peel. Don’t shave the areas that will be treated beginning 24 hours before your peel.
- Arrange for a ride home. If you’ll be sedated during the procedure, arrange for a ride home.
What you can expect
Before the procedure
A chemical peel is usually done at an office or in an outpatient surgical facility. Before the procedure, your doctor will clean your face, protect your hair, and cover your eyes with ointment, gauze, tape or goggles.
Pain relief isn’t typically needed for a light chemical peel. If you’re having a medium peel, you might receive a sedative and painkiller. For a deep peel, you might have a sedative, something to numb the treatment area and fluids delivered through a vein.
During the procedure
During a light chemical peel:
- Your doctor will use a brush, cotton ball, gauze or sponge to apply a chemical solution typically containing glycolic acid or salicylic acid. The treated skin will begin to whiten.
- You might feel mild stinging while the chemical solution is on your skin.
- Your doctor will apply a neutralizing solution or wash to remove the chemical solution from the treated skin.
During a medium chemical peel:
- Your doctor will use a cotton-tipped applicator or gauze to apply a chemical solution containing trichloroacetic acid, sometimes in combination with glycolic acid. The treated skin will begin to whiten.
- After a few minutes, your doctor will apply cool compresses to soothe treated skin. You might also be given a hand-held fan to cool your skin. No neutralizing solution is needed, however.
- You might feel stinging and burning for up to 20 minutes.
During a deep chemical peel:
- You’ll be given intravenous (IV) fluids, and your heart rate will be closely monitored.
- Your doctor will use a cotton-tipped applicator to apply carbolic acid (phenol) to your skin. Treated skin will begin to turn white or gray.
- To limit your exposure to phenol, your doctor will do the procedure in portions at about 15-minute intervals. A full-facial procedure might take about 90 minutes.
After the procedure
After a chemical peel of any depth, your skin will be red, tight, irritated or swollen. Follow your doctor’s directions for sun protection, cleansing, moisturizing and applying protective ointments to your skin. And avoid picking, rubbing or scratching your skin. It may take several months before your skin color returns to normal and you can see the full results of the peel.
After a light chemical peel, treated skin will be red, dry and mildly irritated — although these effects might be less noticeable with each repeat treatment. Your doctor might apply a protective ointment, such as petroleum jelly, to soothe the skin. You can usually wear makeup the next day if you wish.
Treated areas take about one to seven days to heal after a light chemical peel. New skin might temporarily be lighter or darker than normal.
After a medium chemical peel, treated skin will be red and swollen. You’ll feel stinging. Your doctor might apply a protective ointment, such as petroleum jelly, to soothe the area and prevent dryness. After five to seven days, you can use cosmetics to cover any redness.
Use ice packs for comfort. Over-the-counter pain-relieving medication, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve, others), may help reduce any discomfort. You’ll likely schedule a checkup soon after your treatment so that your doctor can monitor your healing.
As swelling decreases, treated skin will begin to form a crust and might darken or develop brown blotches. Treated areas take about seven to 14 days to heal after a medium chemical peel, but redness might last for months.
After a deep chemical peel, you’ll experience severe redness and swelling. You’ll also feel burning and throbbing, and the swelling may even make your eyelids swell shut.
Your doctor will apply a surgical dressing to treated skin. He or she might also prescribe painkillers. You’ll need to soak the treated skin and apply ointment several times a day for about two weeks.
Treated areas will develop new skin within about two weeks after a deep chemical peel, although redness might last for months. Treated skin might become darker or lighter than normal or lose the ability to tan.
You might prefer to remain at home while you’re healing from a chemical peel. You’ll likely need several follow-up visits soon after your treatment so that your doctor can monitor your healing.
Once new skin completely covers the treated area in about two weeks, you can use cosmetics to conceal any redness. Use sunscreen every day.
Results
A light chemical peel improves skin texture and tone and lessens the appearance of fine wrinkles. The results are subtle but increase with repeated treatments. If you have a medium chemical peel, treated skin will be noticeably smoother. After a deep chemical peel, you’ll see a dramatic improvement in the look and feel of treated areas. Results may not be permanent. Over time, age and new sun damage can lead to new lines and skin color changes.
With all peels, the new skin is temporarily more sensitive to the sun. Talk with your doctor about how long to protect your skin from the sun.
Chemical Peel Benefits
A light chemical peel improves skin texture and tone and lessens the appearance of fine wrinkles. The results are subtle but increase with repeated treatments. If you have a medium chemical peel, treated skin will be noticeably smoother
A chemical peel is a procedure in which a chemical solution is applied to the skin to remove the top layers. The skin that grows back is smoother. With a light or medium peel, you may need to undergo the procedure more than once to get the desired results.
Chemical peels are used to treat wrinkles, discolored skin and scars — usually on the face. They can be done alone or combined with other cosmetic procedures. And they can be done at different depths, from light to deep. Deeper chemical peels offer more-dramatic results but also take longer to recover from.
Why it’s done
A chemical peel is a skin-resurfacing procedure. Depending on the issues you’re addressing with the procedure, you’ll choose a chemical peel in one of three depths:
- Light chemical peel. A light (superficial) chemical peel removes the outer layer of skin (epidermis). It’s used to treat fine wrinkles, acne, uneven skin tone and dryness. You might have a light peel every two to five weeks.
- Medium chemical peel. A medium chemical peel removes skin cells from the epidermis and from portions of the upper part of your middle layer of skin (dermis). It’s used to treat wrinkles, acne scars and uneven skin tone. You might need to repeat the procedure to achieve or maintain the desired result.
- Deep chemical peel. A deep chemical peel removes skin cells even deeper. Your doctor might recommend one for deeper wrinkles, scars or precancerous growths. You won’t need repeat procedures to get the full effect.
Chemical peels can’t remove deep scars or wrinkles or tighten sagging skin.
Risks
A chemical peel can cause various side effects, including:
- Redness, scabbing and swelling. Normal healing from a chemical peel involves redness of the treated skin. After a medium or deep chemical peel, redness might last for a few months.
- Scarring. Rarely, a chemical peel can cause scarring — typically on the lower part of the face. Antibiotics and steroid medications can be used to soften the appearance of these scars.
- Changes in skin color. A chemical peel can cause treated skin to become darker than normal (hyperpigmentation) or lighter than normal (hypopigmentation). Hyperpigmentation is more common after superficial peels, while hypopigmentation is more common after a deep peel. These problems are more common in people with brown or black skin and can sometimes be permanent.
- Infection. A chemical peel can lead to a bacterial, fungal or viral infection, such as a flare-up of the herpes virus — the virus that causes cold sores.
- Heart, kidney or liver damage. A deep chemical peel uses carbolic acid (phenol), which can damage heart muscle and cause the heart to beat irregularly. Phenol can also harm the kidneys and liver. To limit exposure to phenol, a deep chemical peel is done a portion at a time, in 10- to 20-minute intervals.
A chemical peel isn’t for everyone. Your doctor might caution against a chemical peel or certain types of chemical peels if you:
- Have taken the oral acne medication isotretinoin (Myorisan, Claravis, others) in the past six months
- Have a personal or family history of ridged areas caused by an overgrowth of scar tissue (keloids)
- Are pregnant
- Have frequent or severe outbreaks of cold sores
How you prepare
Choose a doctor with knowledge of the skin and procedure — a dermatologist or dermatologic surgeon. Results can be variable and depend on the expertise of the person doing the peel. Improperly done, a chemical peel can result in complications, including infection and permanent scars.
Before you have a chemical peel, your doctor will likely:
- Review your medical history. Be prepared to answer questions about current and past medical conditions and any medications you are taking or have taken recently, as well as any cosmetic procedures you’ve had.
- Do a physical exam. Your doctor will inspect your skin and the area to be treated to determine what type of peel you might benefit from most and how your physical features — for example, the tone and thickness of your skin — might affect your results.
- Discuss your expectations. Talk with your doctor about your motivations, expectations and potential risks. Make sure you understand how many treatments you might need, how long it’ll take to heal and what your results might be.
Before your peel, you might also need to:
- Take antiviral medication. Your doctor might prescribe an antiviral medication before and after treatment to help prevent a viral infection.
- Use a retinoid cream. Your doctor might recommend using a retinoid cream, such as tretinoin (Renova, Retin-A) for a few weeks before treatment to help with healing.
- Use a bleaching agent. Your doctor might recommend using a bleaching agent (hydroquinone), a retinoid cream, or both before or after the procedure to reduce the risk of side effects.
- Avoid unprotected sun exposure. Too much sun exposure before the procedure can cause permanent irregular pigmentation in treated areas. Discuss sun protection and acceptable sun exposure with your doctor.
- Avoid certain cosmetic treatments and certain types of hair removal. About a week before the peel, stop using hair removal techniques such as electrolysis or depilatories. Also, avoid hair dying treatments, permanent-wave or hair-straightening treatments, facial masks, or facial scrubs in the week before your peel. Don’t shave the areas that will be treated beginning 24 hours before your peel.
- Arrange for a ride home. If you’ll be sedated during the procedure, arrange for a ride home.
What you can expect
Before the procedure
A chemical peel is usually done at an office or in an outpatient surgical facility. Before the procedure, your doctor will clean your face, protect your hair, and cover your eyes with ointment, gauze, tape or goggles.
Pain relief isn’t typically needed for a light chemical peel. If you’re having a medium peel, you might receive a sedative and painkiller. For a deep peel, you might have a sedative, something to numb the treatment area and fluids delivered through a vein.
During the procedure
During a light chemical peel:
- Your doctor will use a brush, cotton ball, gauze or sponge to apply a chemical solution typically containing glycolic acid or salicylic acid. The treated skin will begin to whiten.
- You might feel mild stinging while the chemical solution is on your skin.
- Your doctor will apply a neutralizing solution or wash to remove the chemical solution from the treated skin.
During a medium chemical peel:
- Your doctor will use a cotton-tipped applicator or gauze to apply a chemical solution containing trichloroacetic acid, sometimes in combination with glycolic acid. The treated skin will begin to whiten.
- After a few minutes, your doctor will apply cool compresses to soothe treated skin. You might also be given a hand-held fan to cool your skin. No neutralizing solution is needed, however.
- You might feel stinging and burning for up to 20 minutes.
During a deep chemical peel:
- You’ll be given intravenous (IV) fluids, and your heart rate will be closely monitored.
- Your doctor will use a cotton-tipped applicator to apply carbolic acid (phenol) to your skin. Treated skin will begin to turn white or gray.
- To limit your exposure to phenol, your doctor will do the procedure in portions at about 15-minute intervals. A full-facial procedure might take about 90 minutes.
After the procedure
After a chemical peel of any depth, your skin will be red, tight, irritated or swollen. Follow your doctor’s directions for sun protection, cleansing, moisturizing and applying protective ointments to your skin. And avoid picking, rubbing or scratching your skin. It may take several months before your skin color returns to normal and you can see the full results of the peel.
After a light chemical peel, treated skin will be red, dry and mildly irritated — although these effects might be less noticeable with each repeat treatment. Your doctor might apply a protective ointment, such as petroleum jelly, to soothe the skin. You can usually wear makeup the next day if you wish.
Treated areas take about one to seven days to heal after a light chemical peel. New skin might temporarily be lighter or darker than normal.
After a medium chemical peel, treated skin will be red and swollen. You’ll feel stinging. Your doctor might apply a protective ointment, such as petroleum jelly, to soothe the area and prevent dryness. After five to seven days, you can use cosmetics to cover any redness.
Use ice packs for comfort. Over-the-counter pain-relieving medication, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve, others), may help reduce any discomfort. You’ll likely schedule a checkup soon after your treatment so that your doctor can monitor your healing.
As swelling decreases, treated skin will begin to form a crust and might darken or develop brown blotches. Treated areas take about seven to 14 days to heal after a medium chemical peel, but redness might last for months.
After a deep chemical peel, you’ll experience severe redness and swelling. You’ll also feel burning and throbbing, and the swelling may even make your eyelids swell shut.
Your doctor will apply a surgical dressing to treated skin. He or she might also prescribe painkillers. You’ll need to soak the treated skin and apply ointment several times a day for about two weeks.
Treated areas will develop new skin within about two weeks after a deep chemical peel, although redness might last for months. Treated skin might become darker or lighter than normal or lose the ability to tan.
You might prefer to remain at home while you’re healing from a chemical peel. You’ll likely need several follow-up visits soon after your treatment so that your doctor can monitor your healing.
Once new skin completely covers the treated area in about two weeks, you can use cosmetics to conceal any redness. Use sunscreen every day.
Results
A light chemical peel improves skin texture and tone and lessens the appearance of fine wrinkles. The results are subtle but increase with repeated treatments. If you have a medium chemical peel, treated skin will be noticeably smoother. After a deep chemical peel, you’ll see a dramatic improvement in the look and feel of treated areas. Results may not be permanent. Over time, age and new sun damage can lead to new lines and skin color changes.
If you’ve got rosacea, then you likely know that one of the last things you should do when it comes to skin care is overexfoliate. Since rosacea is a chronic inflammatory condition that results in a compromised skin barrier, it makes sense to want to avoid exfoliation all together – especially chemical peels – at all costs.
However, chemical peels in a clinic can be perfectly safe for those with rosacea (of course, depending on your specific condition, as everyone’s manifests differently). In fact, a gentler peel can have really great benefits for managing the condition along with other treatments – but only in a professional setting with someone who understands the complexities of rosacea.
We spoke with Spirithoula Koukoufikis, Skinfluencer skin clinic’s senior medical aesthetician to find out exactly how you can get the benefits of a chemical peel for rosacea without causing any adverse effects on your condition.
What Exactly Is Rosacea?
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition, affecting one in 10 people in the UK, that presents in a number of ways. There are various “types” of rosacea, including erythematotelangiectatic rosacea (redness), papulopustular rosacea (acne rosacea), phymatous rosacea (thickening of the skin), and ocular rosacea (symptoms of the eyes). Each of the rosacea types can come in varying degrees of severity, and people can experience more than one. Symptoms can include facial redness and flushing, pimples and bumps, visible blood vessels, sensitivity, sore eyelids, and a burning or stinging feeling.
What Is a Chemical Peel?
A professional chemical peel is a treatment done at a clinic (not at home) in which a practitioner will apply a solution made up of different types of acids in various pH levels to your face. Peels come in three depths – superficial, medium, and deep – each with varying outcomes and aftercare instruction. The aim of a chemical peel is to deeply exfoliate the skin and improve the overall skin texture, tone, and appearance, depending on your goals. It’s important to visit a trained professional who can take into account your skin type and skin tone to find a treatment plan best suited to your individual needs.
What Professional Peels Work Well For Someone With Rosacea?
When it comes to chemical peels for rosacea, Koukoufikis explains that it’s not so much “which acid but more a case of the pH of the acid peel chosen”. For a condition like rosacea, only a superficial peel “that does not have an excessively low pH” should be used, as “you only want to remove the surface of the dead skin, before proceeding with laser treatments to manage and improve the appearance of the condition.”
Benefits of Chemical Peels For Rosacea
When it comes to rosacea, chemical peels can help manage redness and breakouts, and reduce inflammation. However, Koukoufikis says they should be used as part of a bigger-picture treatment plan. “I really believe they should only be used to prep the skin before you tackle the rosacea with laser-based treatments.”
How Often Can Someone With Rosacea Get Chemical Peels?
Koukoufikis says you should only have a peel every four to eight weeks, but for a laser treatment, she recommends every four to six weeks because “the vascular network is so dense and needs to be targeted in a specific way.” Once this course has been completed, you’ll likely only need maintenance treatments once or twice a year.
What to Avoid When It Comes to Chemical Peels and Rosacea
Avoid over-resurfacing the skin. “Remember, in the case of rosacea, the skin’s surface is already compromised,” Koukoufikis says. “By using acid peels too often, the skin is unable to heal and repair. In fact, it is highly likely that you will just create more inflammation and enhance the skin’s sensitivity, which will lead to itching. The skin won’t be able to heal fast enough, and this could lead to other skin conditions such as hyperpigmentation and acne, to name but two.”
What Other Treatments Can Be Used With Chemical Peels For Rosacea?
As Koukoufikis mentioned, she believes the best treatments for rosacea are peels combined with lasers. “Laser treatments that are specifically designed to target vascularity are great for rosacea. Over the years, rosacea will bring more vascularity to the surface of the skin, resulting in the appearance of thread veins or an overall blush/redness, depending on what’s happening beneath the skin,” she says. “You can never take away rosacea, you can only treat it so the appearance of it is improved. The gold-standard treatment protocol for rosacea is laser, and with its advanced technology, Cutera’s Excel V+ is the current industry leader. Excel V+ has been designed to target the excess haemoglobin that manifests as red veins or blushing.”
For that reason, Koukoufikis always recommends a course of laser treatments to “chip away at that dense vascular network, which will improve the overall tone and texture of the skin.” Of course, all of this needs to be in addition to proper skin care at home, curated with you and for you by a skin specialist.
“Rosacea is a complicated skin condition, and really you need a professional to assess and analyse the skin, determine the severity of the rosacea, and prescribe a programme that includes treatments and products to ensure you get the best possible outcome,” Koukoufikis adds.
Final Thoughts on Chemical Peels and Rosacea
In-clinic acid peels can have a wonderful outcome on those with rosacea but are typically best when used in conjunction with other treatments. “They should only be used to prep the skin before you tackle the rosacea with laser-based treatments,” Koukoufikis says.
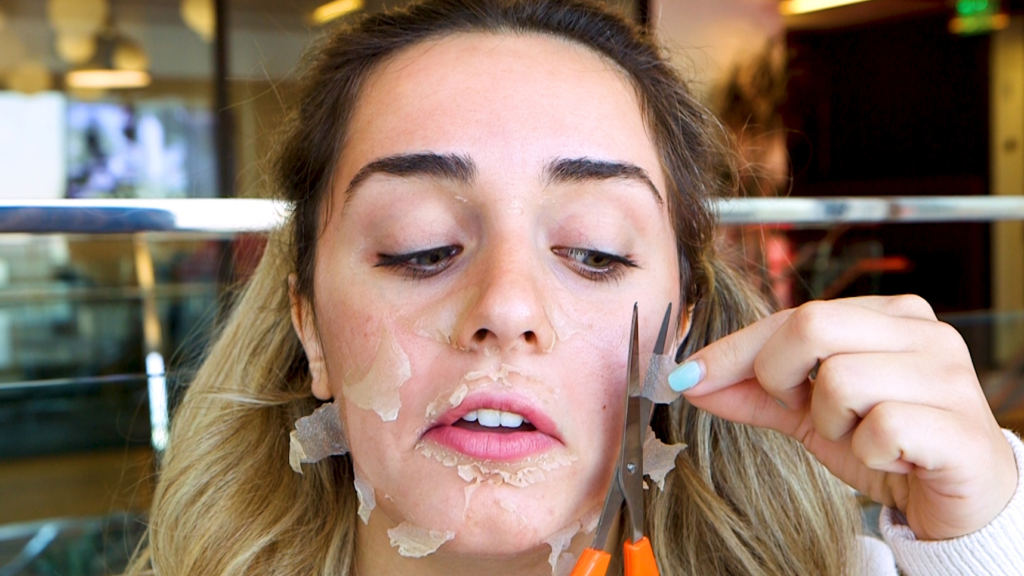

Chemical Peel For Scars On Legs
Chemical Peel – Chemical peel for scars on legs is a safe treatment for reducing mild scarring, by using a plant-based solution. It triggers controlled exfoliation and skin renewal by removing the damaged layers and revealing the new skin that is visibly smoother and noticeably less irregular in colour and texture.
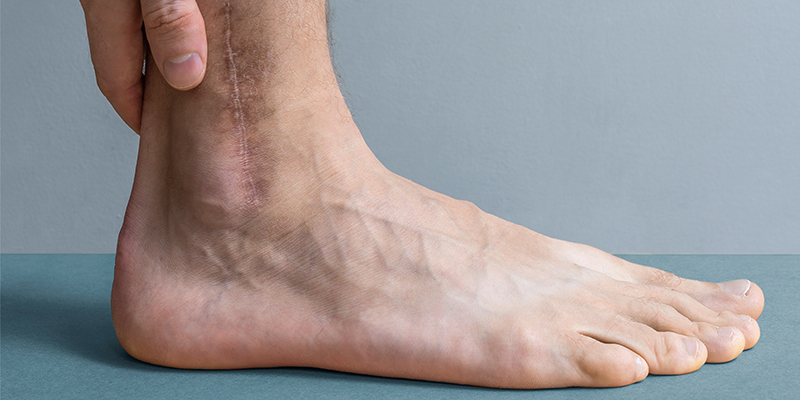
Scars and marks on legs are not uncommon. Tanning, pigmentation, underlying hormonal changes or certain skin conditions, injuries and allergies can result in the appearance of scars. Even though these scars do not impact your overall health, some people may find them a significant aesthetic concern. If you have scars on your legs, read this article to know about the safe and effective treatments for getting rid of them right here!
- What Are The Causes Of Scars On Legs?
- Do Scar Removal Creams Really Work?
- Before And After Results
- How To Prevent Scars On Legs?
What Are The Causes Of Scars On Legs?
Anyone can get a scar as a result of trauma or injury to the skin. Scarring may become more noticeable due to increased production of melanin, a pigment which gives healthy skin its colour. A scar is a sign of your skin’s healing response and does not pose a danger to your overall health.
One of the most common causes of scars on legs is scratching. Itchiness can be a result of dry skin, eczema or poor hygiene. Let’s find out the other causes of scars on legs that may include the following:
- Old Hair Removal Methods – Individuals with thick and dense body hair may be prone to scarring on the legs as a result of ingrowth caused by the use of conventional hair removal methods like waxing, epilation and shaving. Besides, associated skin inflammation may cause localised infection and subsequent scarring. Several women choose to shave unwanted hair and suffer from cuts leading to razor scars on the legs, which may vary in size and appearance based on the severity and depth of the scrape.
- Mosquito/Bug Bites – Insect bites by bed bugs, mosquitoes, ants, fleas and flies can make the skin quite itchy, and if scratched excessively, can cause infection and scarring. Scars due to mosquito bites are quite common. Persistent scratching can lead to larger raised bumps called hypertrophic scars in a few.
- Diabetes – High blood sugar levels can adversely affect several organs of the body, including the skin, especially on extremities. Minor cuts and wounds take much longer to heal and may leave scars due to poor circulation and nerve damage associated with diabetes.
- Skin Diseases – Conditions such as chickenpox, lichen planus, eczema, psoriasis, folliculitis, drug rash and more can lead to dark spots and scars.
- Injuries –Scarring is a sequela of injury, trauma, burn, surgery and vaccination and occurs as a sign of skin healing.
How To Remove Scars On Legs?
Now that you know about the primary causes, it’s time to explore the treatment options for removing the scars on legs.
- Chemical Peel – Chemical peel for scars on legs is a safe treatment for reducing mild scarring, by using a plant-based solution. It triggers controlled exfoliation and skin renewal by removing the damaged layers and revealing the new skin that is visibly smoother and noticeably less irregular in colour and texture. This treatment for scars on legs is more effective than the use of physical exfoliators as it activates the body’s natural response to produce collagen to help fill in the scarred tissue.
https://www.youtube.com/embed/gBypU29ipnA?feature=oembed - Laser Therapy – Laser treatment for scars on legs is an effective method to minimise the appearance and thickness of scars through induction of new collagen. It involves the use of light therapy to remove the outer skin layer. Alternatively, laser scar removal from legs can also stimulate the growth of new skin cells that can reduce the visibility of damaged tissue.
https://www.youtube.com/embed/JxO3cBaT2cg?feature=oembed - Steroid Injections – Dermatologists administer the steroid injections containing triamcinolone directly into the keloidal scars. As a result, the scars become flat and appear less prominent.
- Microdermabrasion – It is a non-invasive procedure to remove the top-most layer of the skin with a specialised tool. This stimulates the healing of the skin making scars less noticeable in a few sessions.
- Dermabrasion – Dermabrasion is a minor surgical and invasive skin resurfacing procedure, which injures the upper and dermal layers of the skin in a controlled manner. Experienced dermatologists perform them in medically-controlled conditions. This method is useful for treating deeper indented scars or acne scars on the legs. Post-procedure, new skin forms which subsequently reduces the appearance of the scarred tissue. This method of scar treatment has become obsolete with the invention of lasers and energy-based devices.
- Skin Lightening Creams – These topical applications reduce the appearance of scars, as they contain various skin lightening agents, which help in reducing the hyperpigmentation associated with the scar, thereby making it less visible. It is best to consult a dermatologist before using one to attain optimal results without any side-effects.
Do Scar Removal Creams Really Work?
Since many scar removal creams flood the market, it’s essential to know if they score over procedural treatments or not to make an informed choice while looking for the best option for scar removal from legs.
- Efficacy – Creams usually take much time to show even mild results. They may be helpful to lighten the marks to a limited extent, but they cannot improve the texture of scars. However, advanced dermatological treatments give quick and visible results by improving both the colour and texture of scars within a few sessions.
- Side-Effects – Creams may contain harsh chemicals, which may not be suitable for your skin. Expert dermatologists perform scar removal treatments to provide safe and effective results.
- Cost – Over the counter, creams and gels may appear cheap at first, but they are just a temporary solution though their outcomes are generally not very apparent. The dermatological treatments are cost-effective, considering their long term effectiveness. These clinically-approved procedures are risk-free treatment options to attain desired results when performed by an experienced dermatologist.
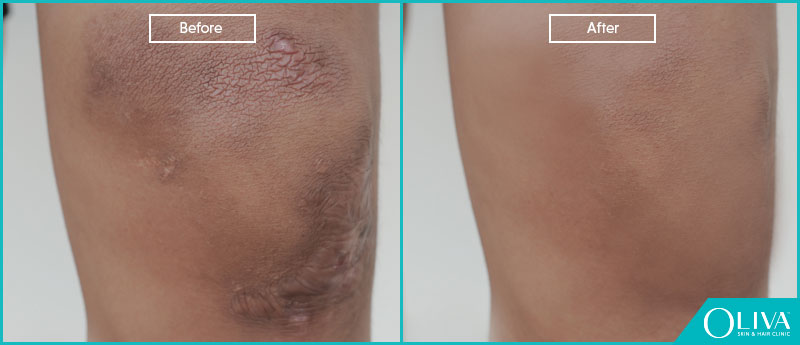
Before And After Results
Professional scar removal treatments help to lighten the appearance of scars on the legs. The below image will give you an idea about the changes you may expect post 6-8 sessions of treatment:
How To Prevent Scars On Legs?
Different types of wounds or injuries warrant various preventive measures to minimise scarring. Here are a few simple tips you can follow to reduce the risk of scarring:
- Rinse the injured area with cold or lukewarm water and allow it to dry.
- To prevent infection, apply an antibacterial ointment using a sterilised applicator.
- Cover the area with a bandage.
- If you notice that the wound is not healing, you should seek medical attention immediately.
- As the wound starts healing, you can use suitable moisturisers to encourage the growth of new skin in the affected area.
- Avoid picking the wound/scab.