The human brain is one of the most remarkable organs in the body, responsible for all our thoughts, actions, and emotions. It’s a complex and fascinating topic that has captivated scientists, researchers, and laypeople alike for centuries. In this article, we’ll explore the incredible workings of the human brain, from its structure and function to the latest research in neuroscience.
Introduction
In this section, we’ll provide a brief overview of the topic and introduce the main points we’ll cover in the article. We’ll also explain why the brain is such an important and fascinating area of study.
The Anatomy of the Brain
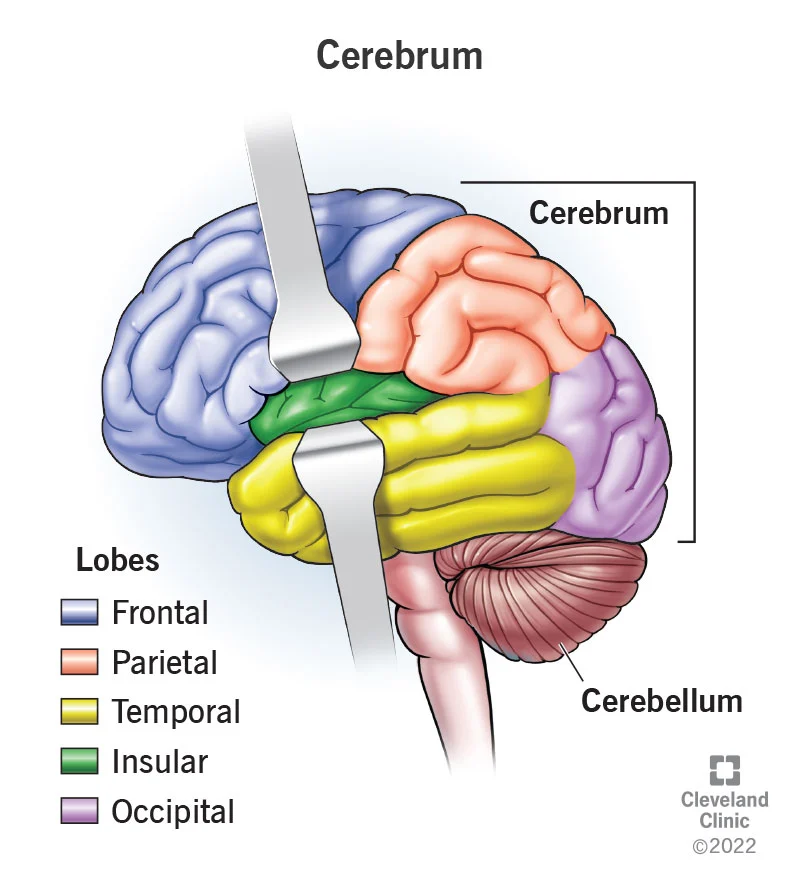
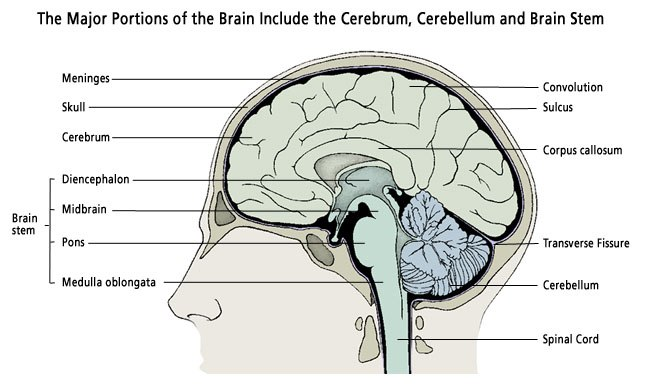
Here, we’ll delve into the physical structure of the brain, including its different regions and their functions. We’ll discuss the three main parts of the brain (the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem), as well as the different lobes (frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital) and their associated functions. We’ll also touch on the role of neurons, the brain’s communication system, and how they work together to create our thoughts and actions.
The Function of the Brain
In this section, we’ll explore how the brain works to control our every move, from our thoughts and emotions to our physical actions. We’ll discuss the role of neurotransmitters and how they affect our mood and behavior, as well as the importance of sleep in maintaining a healthy brain. We’ll also touch on the ways in which the brain can be affected by injury, disease, and other factors.
The Latest Research in Neuroscience
Here, we’ll look at some of the latest advances in neuroscience and how they’re changing our understanding of the brain. We’ll discuss topics such as brain-computer interfaces, neural plasticity, and the potential for brain implants to treat neurological conditions. We’ll also touch on the ethical implications of this research and how it could impact society as a whole.
Common Myths and Misconceptions about the Brain
In this section, we’ll debunk some of the common myths and misconceptions about the brain. We’ll address topics such as the idea that we only use 10% of our brain, whether or not brain training games actually work, and the myth of left-brain vs. right-brain dominance.
The Future of Brain Research
Finally, we’ll look at where the field of neuroscience is headed and what the future might hold for the study of the brain. We’ll discuss the potential for new technologies and treatments, as well as the challenges that lie ahead in understanding this incredibly complex organ.
The study of the brain has always been a fascinating topic for scientists, philosophers, and ordinary people alike. With the advent of modern technology and innovative techniques, the field of brain research has made significant advancements in recent years. But what does the future hold for brain research? In this article, we will explore the latest developments in brain research and the potential implications for our understanding of the brain and its functions.
Technological Advancements in Brain Research
- Neuroimaging Techniques
- Brain-Machine Interfaces
- Optogenetics
- CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Editing
Understanding Brain Function
- Neural Networks and Synaptic Plasticity
- Consciousness and Self-Awareness
- Memory and Learning
- Emotional Processing and Regulation
Brain Disorders and Treatments
- Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Depression and Anxiety
- Traumatic Brain Injury
Ethical and Social Implications of Brain Research
- Brain-Computer Interfaces and Privacy Concerns
- Brain Enhancement and Cognitive Enhancement
- Brain-Computer Interfaces and the Future of Work
- Neuroethics and the Use of Brain Research in Legal Proceedings
Future Directions of Brain Research
- The Connectome and Large-Scale Brain Networks
- Personalized Medicine and Precision Psychiatry
- Brain-Computer Interfaces and Prosthetics
- The Development of Artificial Intelligence and Brain-Inspired Computing
Technological Advancements in Brain Research
Neuroimaging Techniques
One of the most significant advancements in brain research has been the development of neuroimaging techniques. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans can provide detailed images of the brain’s structure and function, allowing researchers to investigate neural networks and identify abnormalities in brain activity associated with various disorders. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) can even be used to track changes in brain activity during cognitive tasks, providing insights into the neural mechanisms underlying human cognition.
Brain-Machine Interfaces
Brain-machine interfaces (BMIs) have the potential to revolutionize the field of neuroscience and transform the way we interact with technology. BMIs enable direct communication between the brain and external devices, allowing individuals to control prosthetic limbs, computer interfaces, and other devices with their thoughts. Researchers are also exploring the use of BMIs for cognitive enhancement, with some studies showing promising results for improving memory and attention.
Optogenetics
Optogenetics is a revolutionary technique that allows researchers to selectively manipulate the activity of neurons in the brain using light. This technology involves genetically modifying neurons to express light-sensitive proteins that can be activated or inhibited by specific wavelengths of light. Optogenetics has already provided valuable insights into the neural basis of behavior and holds potential for developing new treatments for neurological and psychiatric disorders.

CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Editing
CRISPR-Cas9 is a powerful gene editing tool that has opened up new avenues for studying the genetic basis of brain disorders. By editing specific genes associated with brain function, researchers can investigate the role of these genes in neural development and disease. CRISPR-Cas9 also holds promise for developing gene therapies to treat a range of neurological and psychiatric conditions.
Understanding Brain Function
Neural Networks and Synaptic Plasticity
The brain is a complex network of neurons that communicate with each other through synapses. Understanding how these networks operate and how they change in response to experience and learning is a fundamental goal of brain research. Synaptic plasticity refers to the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, a process that is critical for learning and memory.
Consciousness and Self-Awareness
The nature of consciousness and self-awareness is a topic of ongoing debate in the field of neuroscience. Researchers are investigating the neural mechanisms underlying these phenomena, including the role of the prefrontal cortex and other brain regions. Studies of patients with disorders of consciousness, such as coma and locked-in syndrome, are providing new insights into the neural basis of consciousness and the potential for restoring consciousness in these patients.
Memory and Learning
Memory and learning are among the most fascinating functions of the brain. Researchers are exploring the neural mechanisms underlying these processes, including the role of long-term potentiation (LTP) and other molecular and cellular mechanisms. Advances in neuroimaging techniques have also allowed researchers to investigate the neural networks involved in memory and learning.
Emotional Processing and Regulation
Emotional processing and regulation are critical for social and psychological well-being. The amygdala and other brain regions are involved in emotional processing, while the prefrontal cortex plays a key role in regulating emotions. Researchers are investigating the neural mechanisms underlying emotional processing and regulation, as well as the potential for developing new treatments for mood disorders such as depression and anxiety.
Brain Disorders and Treatments
Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia
Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia are among the most common and devastating brain disorders. Researchers are investigating the genetic and environmental factors that contribute to these disorders, as well as potential treatments for slowing or reversing cognitive decline.
Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is a degenerative disorder of the nervous system that affects movement and can cause tremors, stiffness, and other motor symptoms. Researchers are investigating the neural mechanisms underlying Parkinson’s disease, as well as potential treatments for slowing or stopping the progression of the disease.
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures. Researchers are investigating the neural mechanisms underlying epilepsy, as well as potential treatments for preventing or reducing the frequency of seizures.
Depression and Anxiety
Depression and anxiety are among the most common mental health disorders, affecting millions of people worldwide. Researchers are investigating the neural mechanisms underlying these disorders, as well as potential treatments such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and pharmacological interventions.
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a severe mental illness characterized by hallucinations, delusions, and disordered thinking. Researchers are investigating the neural mechanisms underlying schizophrenia, as well as potential treatments such as antipsychotic medications and cognitive-behavioral therapy.
Ethical and Societal Implications of Brain Research
Privacy and Consent
As brain research advances, there are increasing concerns about privacy and consent. Brain data is highly personal and sensitive, raising questions about who should have access to this information and how it should be used.
Neuroethics
Neuroethics is a field of study that explores the ethical and societal implications of brain research. Issues such as cognitive enhancement, brain-machine interfaces, and the use of brain data raise complex ethical questions that require careful consideration.
Neurodiversity
Neurodiversity is a movement that advocates for the acceptance and celebration of neurological differences, such as autism and ADHD. Brain research can contribute to a greater understanding and appreciation of neurodiversity, as well as the development of more effective treatments and interventions.

Social and Economic Impacts
Brain research has the potential to bring about significant social and economic changes, such as new treatments for brain disorders and the development of brain-inspired technologies. However, these changes may also have unintended consequences and raise questions about access, equity, and social justice.
Brain research is a dynamic and rapidly evolving field that holds tremendous potential for our understanding of the brain and its functions. The latest advancements in technology and techniques have allowed us to gain new insights into the workings of the brain, from neural networks and synaptic plasticity to consciousness and emotional processing. With continued progress and innovation, the future of brain research holds great promise for improving our understanding of brain disorders, developing new treatments, and enhancing human cognition and performance.
Conclusion
The human brain is an incredibly complex and fascinating organ, responsible for all our thoughts, actions, and emotions. It’s a topic that has captivated scientists and laypeople alike for centuries, and one that continues to yield new insights and discoveries. By exploring the structure and function of the brain, as well as the latest research in neuroscience, we can deepen our understanding of this remarkable organ and the role it plays in our lives.
FAQs
- What is the most complex part of the brain?
- The cerebral cortex, which is responsible for higher-level cognitive functions such as language, reasoning, and consciousness, is considered to be the most complex part of the brain.
- Can the brain regenerate itself after injury?
- While the brain does have some capacity to repair itself after injury, it’s limited. However, researchers are exploring new treatments and technologies that could help the brain to repair itself more effectively.
- How does the brain process emotions?
- Emotions are processed in the limbic system, which includes the amygdala, hippocampus, and hypothalamus. These regions work together
- How does the brain process emotions?
- Emotions are processed in the limbic system, which includes the amygdala, hippocampus, and hypothalamus. These regions work together to regulate our emotional responses and play a key role in our social and interpersonal interactions.
- Can the brain change its structure and function over time?
- Yes, the brain has the ability to change its structure and function in response to new experiences and learning. This is known as neuroplasticity and is a key area of study in neuroscience.
- What are some common brain disorders?
- Some common brain disorders include Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, epilepsy, and stroke. These conditions can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life and require specialized treatment and care.